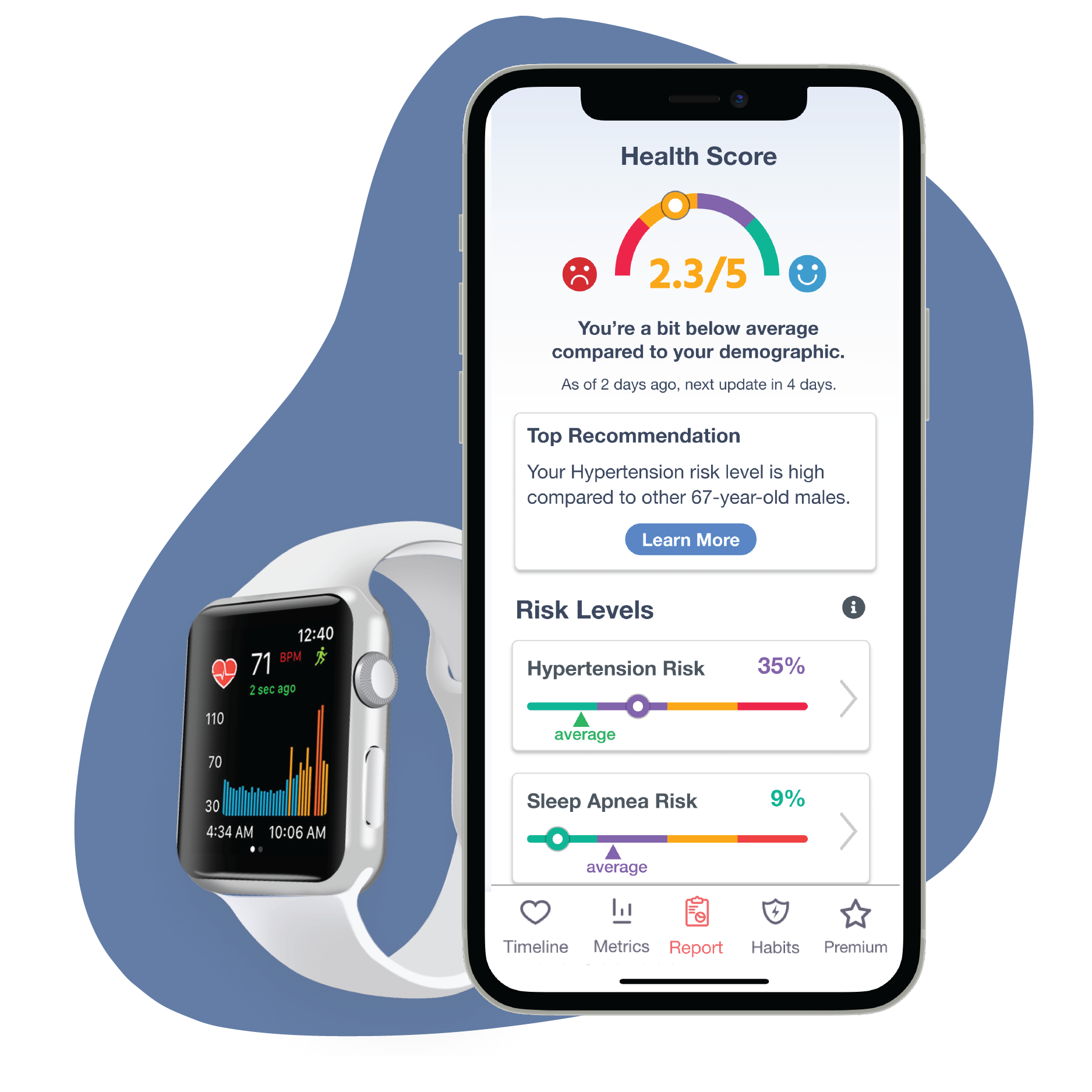
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), more than 6.2 million Americans are living with heart failure.1 This condition is generally the end-stage of most cardiovascular diseases, including chronic blood hypertension, arrhythmias, and coronary artery disease.
There are several types of heart failure, which determine the nature of signs and symptoms you will experience.2 For instance, some people with heart failure have trouble pumping blood to peripheral organs, whereas others develop stiffness of the heart tissue.
While preventing heart failure should be the goal, there is still a lot you can do to continue living a fulfilling life, even with a heart failure diagnosis.

Scientists divide the heart into two parts based on function – The left side and the right side.
When the bottom left chamber of your heart (called the left ventricle) is no longer functioning properly, left-sided heart failure follows.
The right ventricle receives the deoxygenated blood (blood with low O2 concentrations) from the body and sends it to the lungs.
Generally, right-sided heart failure is triggered by left-sided heart failure. Because the blood accumulates in your lungs, the right ventricle has to pump blood against major resistance. Eventually, the structure of the right ventricle changes, leading to heart failure.
Depending on the type of heart failure, the signs and symptoms may vary. However, the most common symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Sudden weight gain
- Anorexia (i.e., appetite suppression)
- Persistent coughing
- Heart palpitations
- Abdominal swelling
- Dyspnea (i.e., shortness of breath)
- Edema (i.e., swelling of the lower limbs)
- Protruding neck veins
Unfortunately, heart failure is a common complication of heart disease. Making lifestyle modifications and adopting a healthy way of eating are essential to ease your symptoms.

Treatment Options for Heart Failure
- A recommended <2 grams of sodium per day
- High fiber, high vegetable diet
- Regular exercise, monitored through a cardiac rehabilitation program
- Cessation of smoking
- Alcohol consumption in moderation
- Medications
- Education regarding symptom management
- Weight monitoring

By making heart healthy lifestyle choices and changes (which reduces heat failure risk factors) will help to prevent the disease. Some of these lifestyle choices include:2
- Engaging in physical activity
- Quitting smoking
- Managing diabetes and hypertension
- Lowering stress levels
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Eating heart healthy foods
- Getting adequate sleep
By leading a heart healthy life, you can prevent heart failure. And even with a diagnosis, you can still use these recommendations to continue leading a fulfilling life.