Obesity has become a real public health issue over the past few decades. The rates of obesity, particularly in modern countries are staggering. In fact, over 40% of all U.S. adults are obese. And, sadly, the negative ripple effects obesity can have on our health and hearts is wide ranging. However, obesity can be prevented and reversed.
Let's look at exactly what obesity is, what causes it, its associated health risks, and prevention methods.
Overview
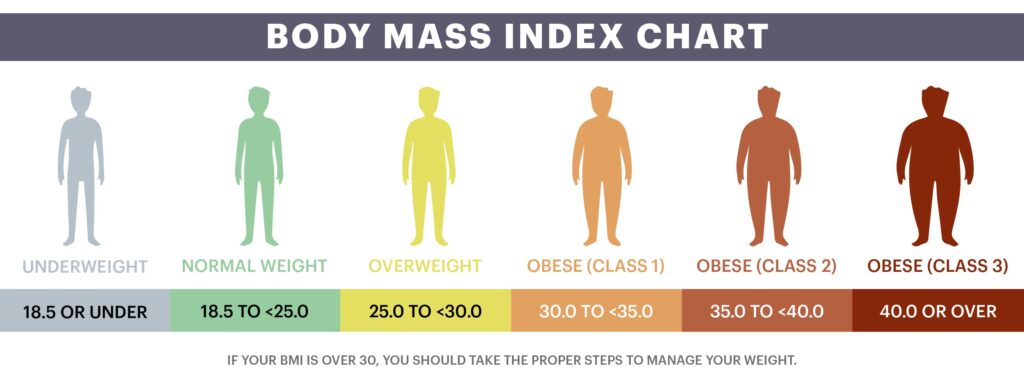
To measure obesity, doctors use a parameter called body mass index (BMI). This parameter takes into consideration the weight and height of the individual as focusing solely on the weight of the person is shortsighted since bodies come in a wide variety of shapes and sizes.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), a BMI that’s above 30 classifies a person as obese.1 Unfortunately, obesity causes a significant risk increase in diabetes, heart disease, cancer, and many other conditions.
In this article, we will cover some general aspects of obesity, as well as its connection to heart disease. But first, let us start with the classification of obesity.

Scientists give different classes of obesity based on your BMI. This helps them assess your risk of certain diseases.
The following classes work for adults older than 20 years old2:

Besides a few medical conditions, researchers only cite risk factors of obesity, not direct causes.
Some of the risk factors that predispose you to obesity include:
Dietary choices – Consuming calorie-dense foods, such as vending machine snacks, fast food, and baked goods, may rapidly cause you to gain weight. Soda, fruit juice, and other sugary drinks are also culprits.
Sedentary lifestyle – Living a sedentary lifestyle with little to no physical activity is a risk factor for obesity.
Family factors – Being raised in a family of overweight individuals increases your risk of obesity. Researchers believe that the abundance of calorie-dense foods in the household and the lack of physical activity are the two primary drivers of this phenomenon.3
Psychological factors – Chronic stress predisposes people to obesity. This is more common in people who find comfort in binge eating when dealing with stressful situations.
Socioeconomic factors – Families who live in poor socioeconomic conditions where supermarkets and healthy foods are not available (or expensive) tend to opt for convenience foods (e.g., frozen meals, cookies, crackers). Therefore, they are at a higher risk of obesity.
Certain medications – Medications that increase the risk of obesity are prednisone, gabapentin, amitriptyline, paroxetine, and propranolol.

According to reports, obesity affects more than 40% of Americans. Previously, people thought that having extra fat is harmless. Today, we know otherwise.4
Adipose tissues release chemicals into the blood, which increase the risk of heart disease. Obesity causes low-grade inflammation – A metabolic state that’s responsible for a myriad of diseases. This is more probable when the fat tissues are located on your belly or waist.5
Scientists found that low-grade inflammation alters the sensitivity of your tissues to the action of insulin.6 As a result, you will find it difficult to regulate your blood sugar levels. consequently, you may develop diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
The metabolic syndrome increases the risk of heart disease in the following ways:
Dyslipidemia – High LDL, low HDL, and high triglycerides
Chronic hypertension – Damages the heart chambers and blood vessels, which eventually leads to coronary artery disease or heart failure
Hyperglycemia – A chronic state of elevated blood glucose that damages the heart, brain, eyes, kidneys, and blood vessels
As we mentioned above, obesity puts you at risk of metabolic syndrome. However, other complications of obesity impact every aspect of your life.
You may experience one or more of the following health problems:
- Bone and joint problems
- Dyspnea (i.e., shortness of breath)
- Restless sleep
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Liver and gallbladder disease
- Unhealthy dieting and eating disorders
- Depression
- Increased risk of heart disease and stroke in the future
- Substance abuse

By making healthy lifestyle choices and changes, you can prevent and reverse obesity. Some of these lifestyle choices include:
- Engaging in physical activity
- Quitting smoking
- Managing diabetes and hypertension
- Lowering stress levels
- Eating healthy foods
- Getting adequate sleep
Obesity is a major risk factor for multiple health conditions, including heart disease. Lowering your body mass index (BMI) will have a direct impact on your cardiac function and risk of disease.