A cardiac arrhythmia affects the heart’s physiological rhythm. This is basically a disease that alters the electricity of your heart.
As a result, your heart can beat too fast, too slow, or too early. In some cases, it contracts erratically, which is referred to as fibrillation. According to research, up to 5% of the population may have some type of arrhythmia.1 Unfortunately, many people are unaware of their conditions, which is a direct reason behind sudden cardiac arrest.
- Their heart is skipping beats
- A fluttering sensation in the neck
- Unusually rapid heartbeat
- Irregular heartbeat
- Severe chest pain – Some describe it as an elephant sitting on their chest
- Dyspnea (i.e., shortness of breath)
- Chronic fatigue
- Lightheadedness
- Fainting
- Irregular heartbeat
- Palpitations
- Night sweats
- Low blood pressure
In order to treat an arrhythmia, your doctor will take your medical history, conduct a comprehensive physical examination, and order some tests. The most common test used to diagnose arrhythmias is an electrocardiogram (ECG).
Because there are often long periods where someone with an arrhythmia is asymptomatic, the Cardiogram app can be used to collect long periods of heart rate data which can then be easily shared with a doctor to help with diagnosis. In some cases, a doctor may also suggest wearing a Holter monitor for 24 hours' worth of data collection.
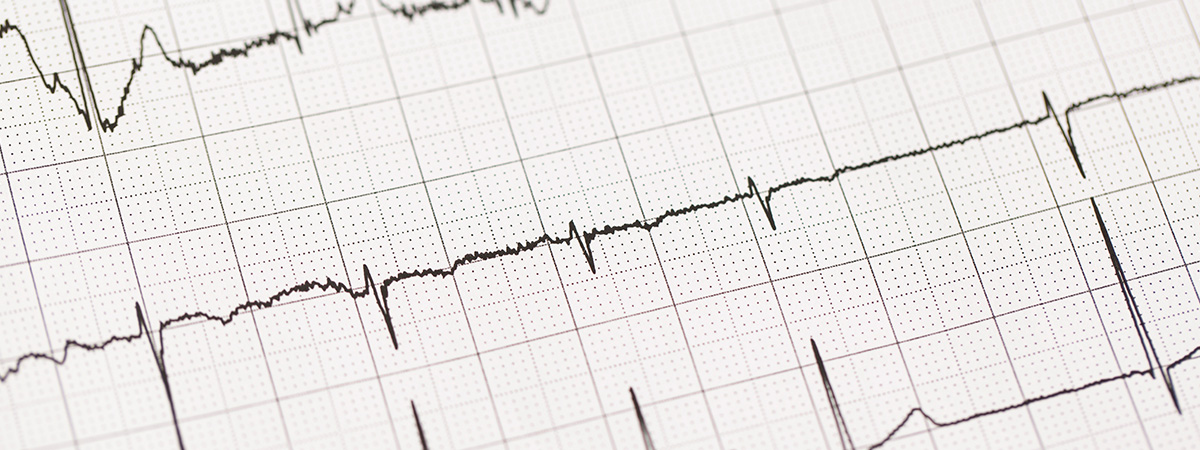
Tachycardic arrhythmias make up a category of electrical issues that accelerate your heart rate to above 100 BPM.
When your heart starts beating too fast, there is little time for the ventricles to fill with blood properly. This may compromise the oxygen and nutrients that reach your tissues.
Generally, a heart rate above 100 bpm is not a cause for alarm if it lasts for a few minutes. However, if you notice that your heart has an irregular rhythm for more than 30 minutes, you should head to the nearest emergency department.2 This is especially necessary if you are also experiencing chest pain.
Ventricular tachycardia is when your heartbeat is faster than 100 bpm. However, the rhythm will originate from the ventricles rather than the atria.
This condition may develop due to coronary artery disease or before a myocardial infarction (i.e., heart attack).
Unlike atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter may not present with any symptoms. This is because the heart has a relatively stable rhythm.
This condition is common in people with other cardiac diseases. It also emerges after open heart surgery, especially within the first week of the operation. While atrial flutter may seem benign, it can be life-threatening without proper management.