- Paroxysmal A-fib is the most common type and typically lasts less than seven days.
- Persistent A-fib lasts longer than seven days but can be controlled with medication or other treatments.
- Permanent A-fib is the least common type and cannot be controlled with medication or other treatments.
- Lone A-fib is a type of atrial fibrillation that occurs in people who have no other heart conditions.


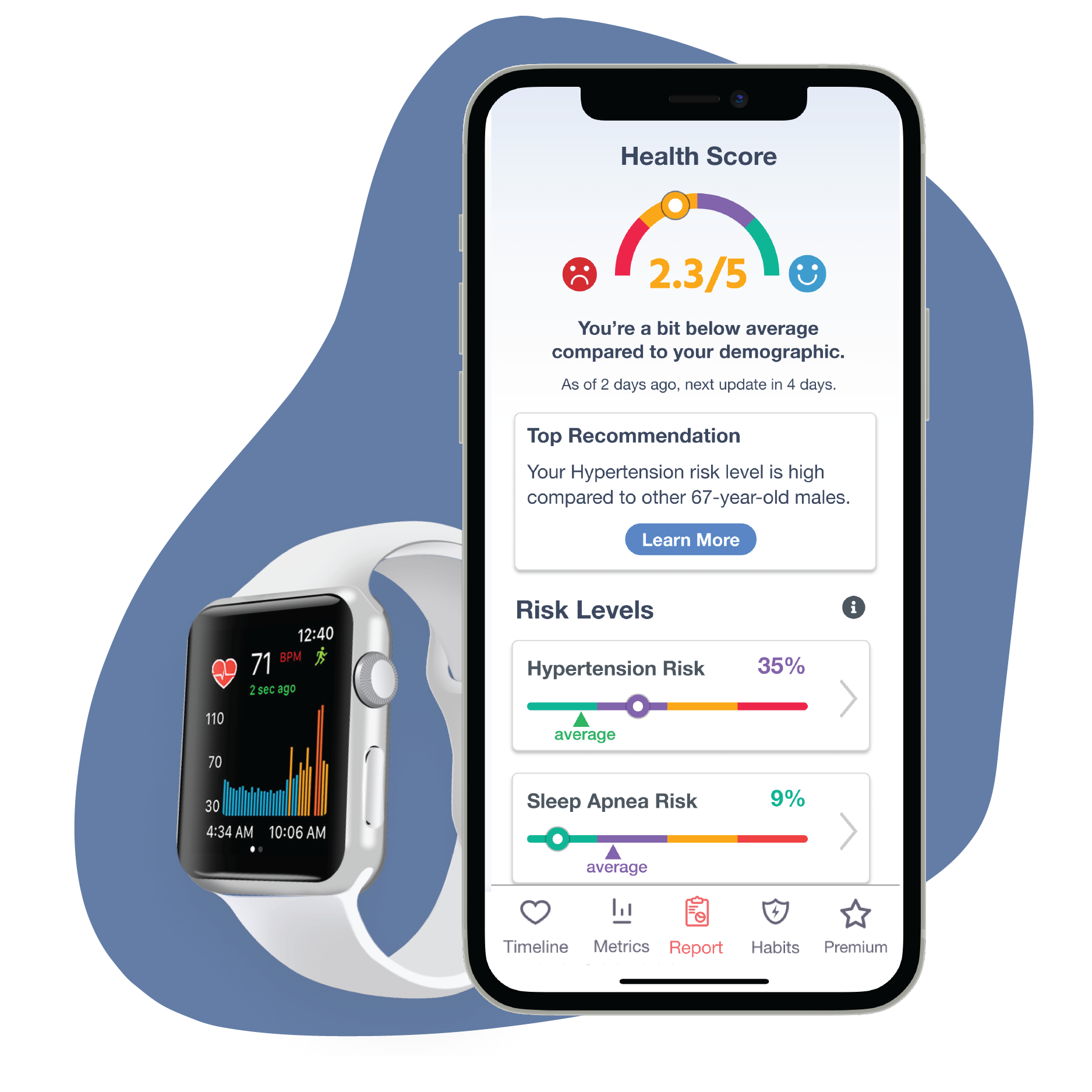
If there’s a chance you have atrial fibrillation, or if you’ve already been diagnosed, Cardiogram allows you to share your heart rate data with your doctor. Sharing this minute-to-minute HR data can help your doctor see and monitor your heart health with greater ease and clarity. And this can result in both faster diagnosis and a more tailored treatment plan.
You can also use Cardiogram to monitor the efficacy of any new medications or treatments tried. Monitoring your heart rate is one of the most important things to track when it comes to diagnosing atrial fibrillation, so let’s see how Cardiogram can help us with that:
Tagging Symptoms
Creating new tags on your heart rate graph when you feel symptoms can help you keep track of your atrial fibrillation. Because atrial fibrillation can present with many symptoms such as palpitations, chest pain, dizziness, fatigue, and shortness of breath, keeping track of your symptoms through tagging can be very beneficial, pinpointing the particular times and frequencies of episodes.
Tracking Symptoms
Whenever you experience recurring symptoms, in addition to tagging, be sure to also hit the “add symptoms” button on your Cardiogram app. This will help you to keep track of your symptoms, and allow your doctor to gauge the frequency and severity of your condition for a more accurate Keeping track of symptoms can also help see if a new medication or treatment plan is working for you, or if there are still things that need to change. Remember, you can always add your own custom symptoms if you experience symptoms not listed.
Journaling
TURN ON HEART RATE ALERTS
Some people with atrial fibrillation have a slow ventricular response (a heart rate that is too slow). To make sure you’re aware of when your heart rate becomes too slow, activate your heart rate alerts. This way, you’ll be notified if your heart rate goes below (or above) your specified threshold.
Join our facebook community
If you have questions or concerns, it's important that you first seek help and advice from your doctor. However, our Cardiogram Community on Facebook is another great resource, filled with other members who share similar experiences and enjoy helping others in the community.
Share data with your doctor
You can easily download CSVs or PDFs of your data to bring to your next doctor's visit. This can help support a diagnosis if you have evidence of symptoms and how they’re impacting your cardiovascular activity. This is why it’s important to make sure you are tagging, journaling, and keeping track of your symptoms on your Cardiogram app.
Participate in Our AFib Project
Our AFib Project is helping our data scientists understand the difference between those with and without atrial fibrillation to improve our algorithms. If you have (or suspect you could have) atrial fibrillation, you can participate in our Afib Project. Learn all about it here.