Magnesium is a humble, yet mighty mineral that plays a substantial role in our overall wellbeing and is also a key player in maintaining our cardiovascular health. In fact, it can help the heart in maintaining its proper rhythm and lowering blood pressure.
Unfortunately, in the United States, nearly half the population is deficient in this essential nutrient, leaving many of us more susceptible to conditions like cardiovascular heart disease (CVD) and arrhythmias.1

While adequate amounts of magnesium can improve heart function, lacking in magnesium can result in several adverse effects on the heart. It can lead to cardiovascular disease in many ways, including these risk factors:6
- Hypertension: As we've mentioned earlier, magnesium plays a crucial role in regulating blood pressure. Insufficient intake of this mineral can lead to elevated blood pressure levels, a risk factor for heart disease.
- Heart Arrhythmias: Irregular heart rhythms are more common in those with low magnesium levels. Arrhythmias can cause a range of complications, from shortness of breath and weakness to more serious conditions like heart failure.
- Coronary Artery Disease: Lower levels of magnesium can increase the risk of atherosclerosis, a condition where the arteries harden and narrow, leading to coronary artery disease.
- Heart Attack: Magnesium deficiency can increase the risk of heart attacks by causing imbalances in the electrical conduction system of the heart and the development of blood clots.

A balanced, heart-healthy diet is the best way to ensure you're getting enough magnesium. Foods that are rich in magnesium include:7
- Green leafy vegetables
- Whole grains
- Nuts
- Legumes
- Dark chocolate
For those who have trouble getting enough magnesium from their diet (which, let’s be honest, is many of us), dietary supplements are also available. However, always remember to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen.

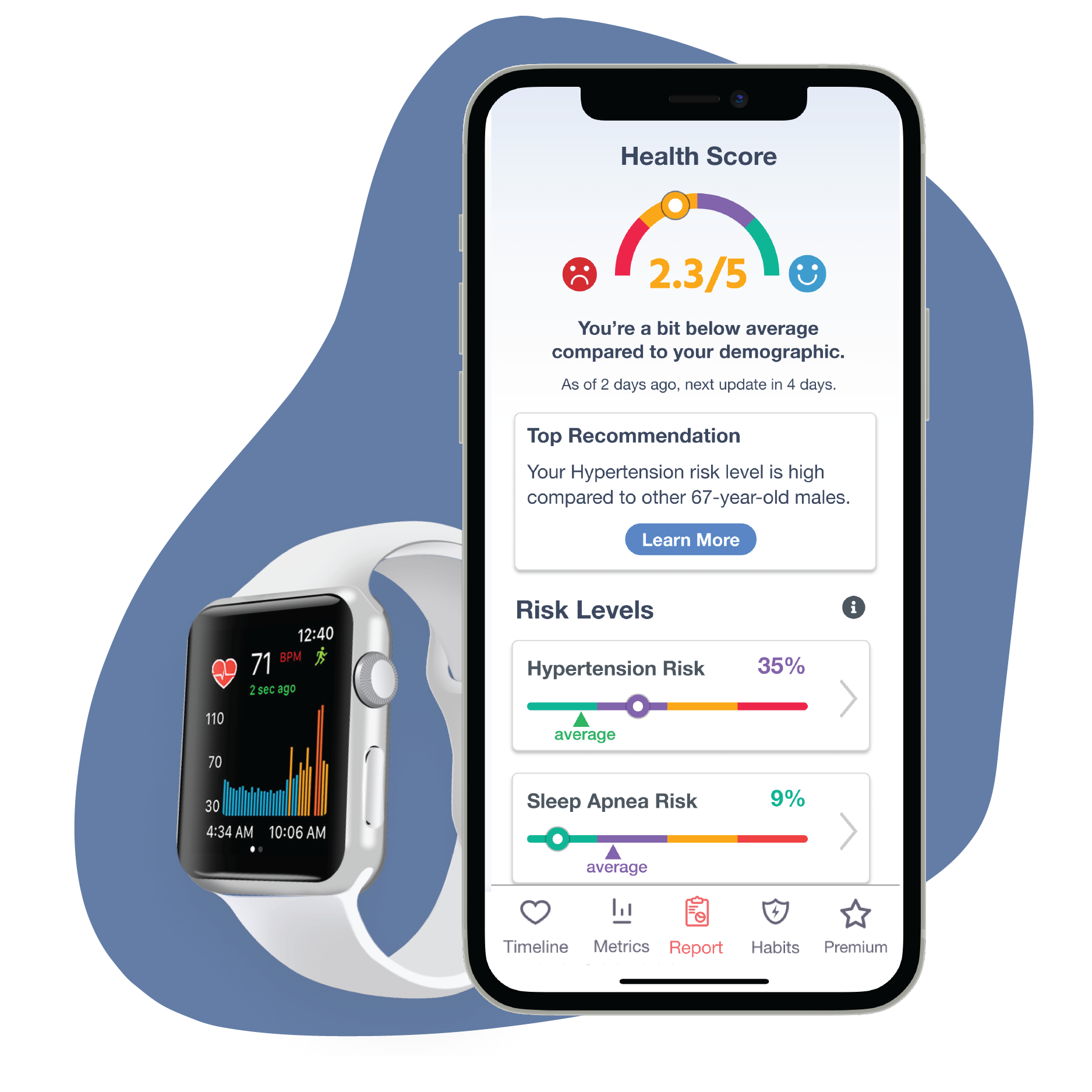
Remember, with the Cardiogram app, you can track your heart rate and monitor any irregularities that could be linked to magnesium deficiency. If you find any irregular heart rate patterns, or if you’ve already been diagnosed with an arrhythmia, see if you begin to notice a difference after intaking the right amounts of magnesium, as recommended by your physician.
Helpful Hint: Create a tag on the days that you take magnesium to get a full picture of how magnesium impacts your heart specifically and over time. Better yet? You can then share this data with your doctor.
With the combination of Cardiogram and a magnesium-rich diet, you'll be on your way to improved cardiovascular health and better control over it in no time
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5786912/#:~:text=Moreover%2C%20around%20half%20(48%25),amount%20of%20magnesium%20from%20food
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Magnesium-Consumer/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11105328/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7524176/#:~:text=Administration%20of%20300%20mg%2Fdaily,compared%20to%20placebo%20received%20groups.
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28180945/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2721016/
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/15650-magnesium-rich-food